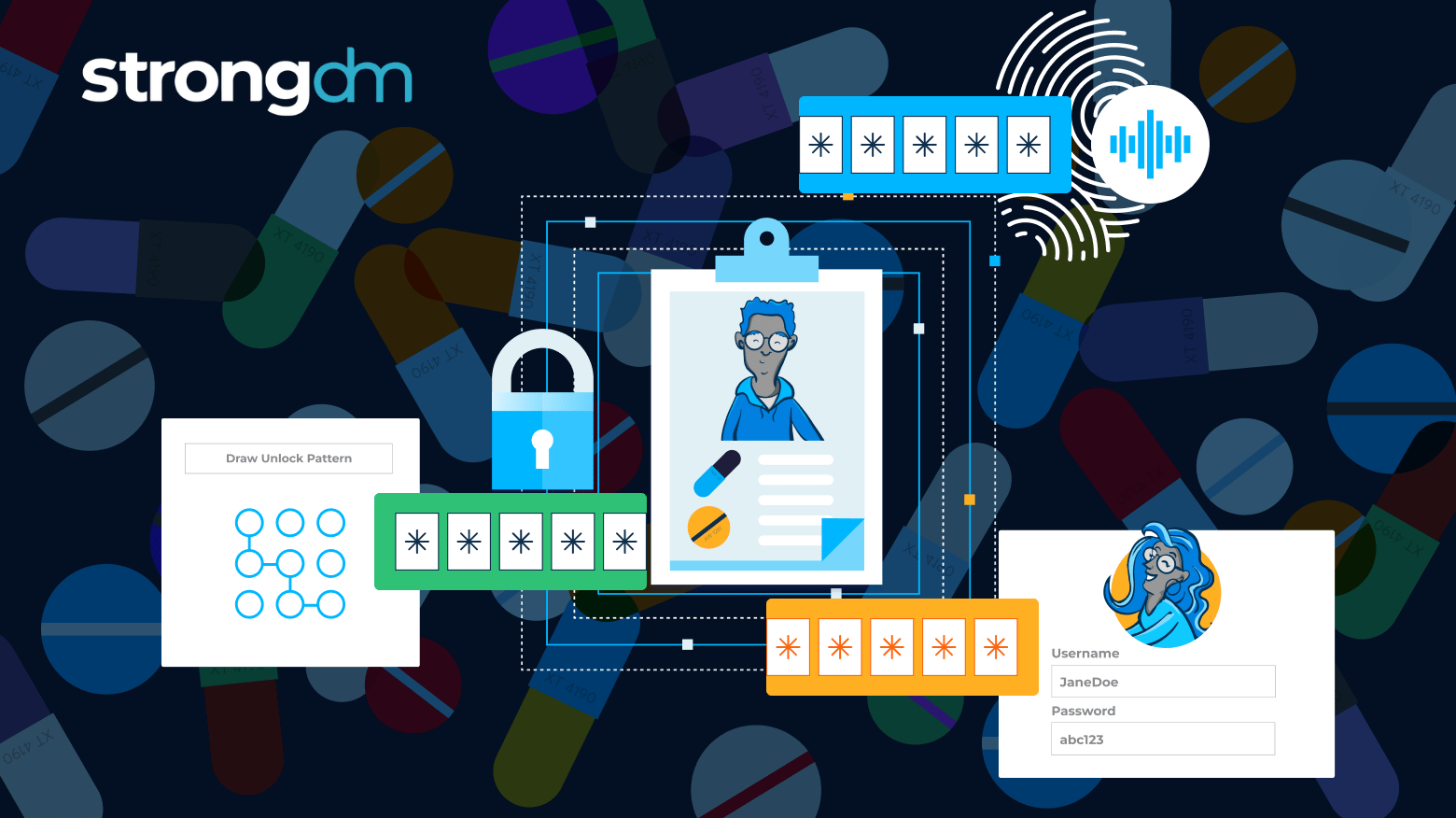
The HIPAA Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) requirement is a security measure that requires users to verify their identity using at least two different factors—such as something they know (a password), something they have (a smartphone or token), or something they are (a fingerprint)—to access systems containing electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI). This additional layer of security is designed to protect sensitive healthcare data from unauthorized access, even if one credential is
Posts by Category:
- Security
- Access
- DevOps
- Privileged Access Management
- Auditing
- Zero Trust
- Compliance
- Policy
- Databases
- SOC 2
- Authentication
- Identity and Access Management
- Team
- Compare
- Engineering
- Integrations
- Product
- Kubernetes
- AWS
- Productivity
- Podcasts
- SSH
- Observability
- HIPAA
- ISO 27001
- Role-Based Access Control
- Dynamic Access Management
- Secure Access Service Edge
- Webinars
- Events
- NIST
- Onboarding
- Passwordless
- Offsites
- Platform
- PCI
If organizations hope to minimize their exposure to attacks and mitigate any damage done by a threat, they must have a comprehensive incident response plan. An effective plan will detect, contain, and enable rapid recovery from security breaches, preserving your business continuity and operability. We've outlined seven incident response steps for you to follow so you can be prepared for a threat.
Protecting sensitive patient data in healthcare isn't just a priority—it's a legal and ethical obligation. However, one of the most overlooked security gaps that healthcare organizations face is the practice of password sharing among employees. This seemingly harmless habit can quickly lead to unauthorized access and serious data breaches, putting both the organization and patients at risk. While often seen as a convenient shortcut, password sharing undermines the security of protected health
The HIPAA Omnibus Rule strengthens privacy and security protections for patient health information, extends liability to business associates, and increases penalties for non-compliance.
Healthcare data security protects sensitive patient information and related data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. The effective implementation of healthcare data security requires implementing cybersecurity measures to ensure healthcare data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It must also include compliance with relevant regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).

Following a HIPAA compliance checklist can help HIPAA-covered entities comply with the regulations and become HIPAA compliant. In this HIPAA compliance guide, we’ll review the 8 primary steps to achieving HIPAA compliance, tips on how to implement them, and frequently asked questions.
HITRUST and HIPAA often go hand-in-hand when talking about security compliance. But what are they, and how do they compare? In this article, we’ll review HITRUST vs. HIPAA, including their differences, similarities, and advantages, and we’ll explain how and when to use them in compliance efforts.
While HIPAA rules benefit both patients and providers, failure to comply with these standards can have significant downsides for both parties. That’s why it is important to understand how HIPAA works and the key areas it covers. Read on to discover the three rules of HIPAA and how you can apply them to help your organization ensure compliance.
This article gives you a broad look at the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) minimum necessary standard. You’ll learn about its requirements, exceptions, and how to implement it.
This article digs into Health Care Accountability and Portability Act (HIPAA) violations. Discover what they are and get examples of typical HIPAA violations in healthcare. Plus, learn how breaches are detected and reported and what you can do to protect your organization.
This article breaks down the different HIPAA penalties—including civil and criminal penalties—and the maximum penalties for HIPAA violations. Find out who is liable under HIPAA, what the most common HIPAA violations are, and how to ensure compliance and prevent HIPAA violations in your own organization.