7 Cyber Insurance Requirements (And How to Meet Them)


Written by
Schuyler BrownLast updated on:
June 26, 2025Reading time:
Contents
Built for Security. Loved by Devs.
- Free Trial — No Credit Card Needed
- Full Access to All Features
- Trusted by the Fortune 100, early startups, and everyone in between
The increase in data breaches, ransomware, and other cyber attacks that marked the pandemic and remote work era motivated organizations to turn to cybersecurity insurance to mitigate their financial and cyber liability risks.
Since then, the emergent cyber insurance market has grown and evolved. Now, organizations must meet comprehensive cyber insurance requirements to qualify for coverage. This article defines seven key cybersecurity insurance requirements. Adhering to these requirements will ensure you’ve covered your bases in case of a claim.
1. Strong Access Controls
Insurers may require businesses to have strong access controls. These controls mitigate the threat of cybercrimes arising from unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems. Such crimes might include phishing attacks and cyber extortion.
Access controls exist within an overall data protection framework that uses authentication and authorization rules to:
- Determine which information a particular user has permission to access.
- Verify the user’s identity.
How access controls are applied and enforced varies from organization to organization. In ascending order of complexity, the three most commonly used frameworks are:
- Discretionary access control (DAC)
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Attribute-based access control (ABAC)
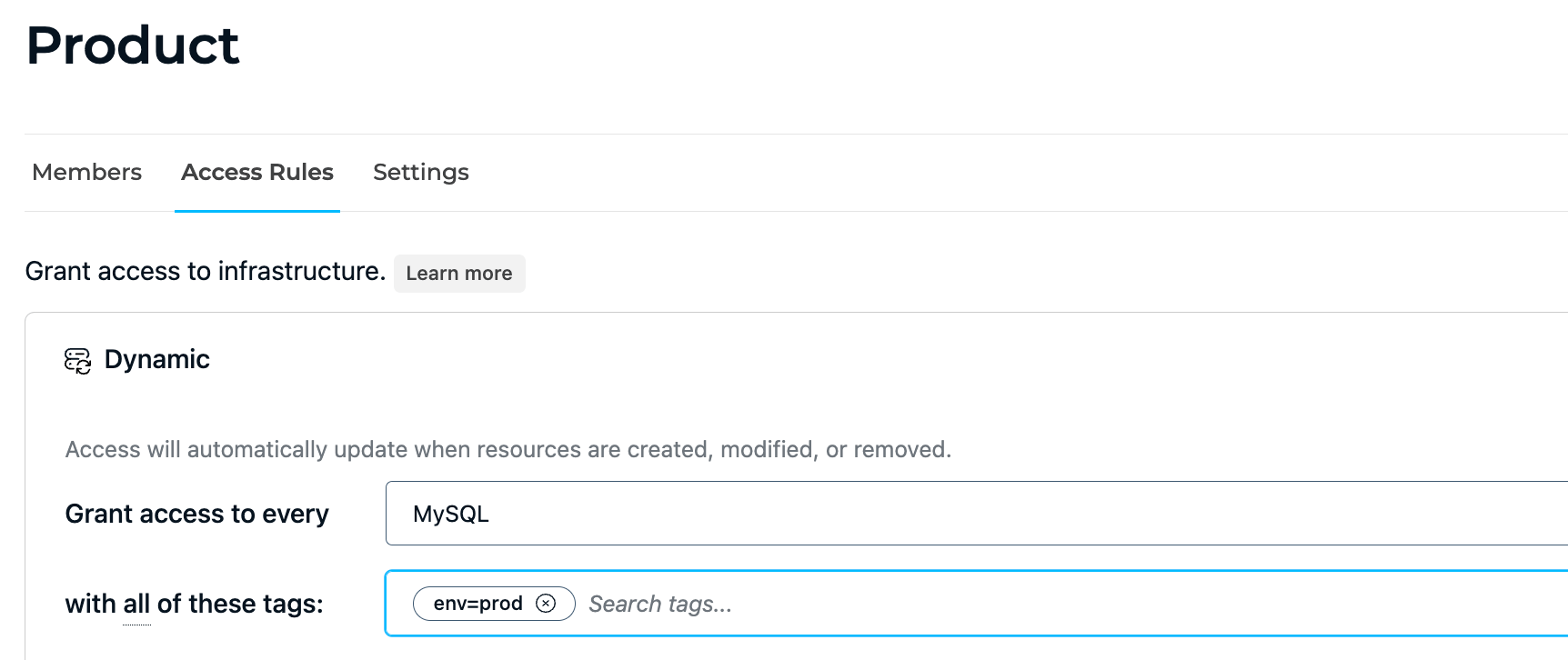
💡Make it easy: StrongDM allows you to create dynamic access rules to implement attribute-based access control. Create tags for regions or environments so only a certain role can request access to critical environments like prod. Try it yourself.
Organizations will use these frameworks singly or in combination, depending on their approach to risk management. Your company’s size, appetite for managing complexity, and privacy protection policies are among the factors to consider when selecting a framework.
2. Regular Vulnerability Assessments
Insurers may require businesses to conduct regular vulnerability assessments to identify and remediate system weaknesses that threaten data security.
Data breaches, for example, in an overwhelming proportion of cases, result from authentication vulnerabilities. The main culprits: weak or stolen credentials. Errors in coding or logic may also breed authentication vulnerabilities.
Authentication vulnerabilities allow malicious actors to circumvent the authentication process and gain access to protected systems and user accounts. Posing as legitimate users, they can steal or manipulate critical data, complete fraudulent transactions, and destroy entire systems.
The recent cyberattack on ION Trading UK is a case in point. The attack originated from a Russian ransomware gang and briefly halted electronic derivatives trading across the UK and Europe. Network interruption during the attack materially affected the ability of futures traders to estimate margins. Two days later, firms still struggled to resolve the backup in transactions resulting from the attack.
Costly business interruptions and reputational loss are not the only risks facing organizations that suffer data breaches. Third-party liability claims against the organization are likely. And where data is governed by GDPR, financial, or other regulations, there may be legal consequences, too.
3. Incident Response Plan
Insurers may require businesses to have a well-defined incident response plan to quickly and effectively respond to cyberattacks and mitigate their impact.
An incident response plan documents your organization’s processes and procedures when a potential incident is detected. These corrective actions serve to contain a situation that is already occurring and limit the damage.
A comprehensive plan should define who to notify in the event of an incident and the channels to use. It will also describe what information to gather during the incident. Finally, it will provide a taxonomy for the categorization of each incident.
A solid incident response plan will also include a post-mortem and root cause analysis once staff has resolved an incident.
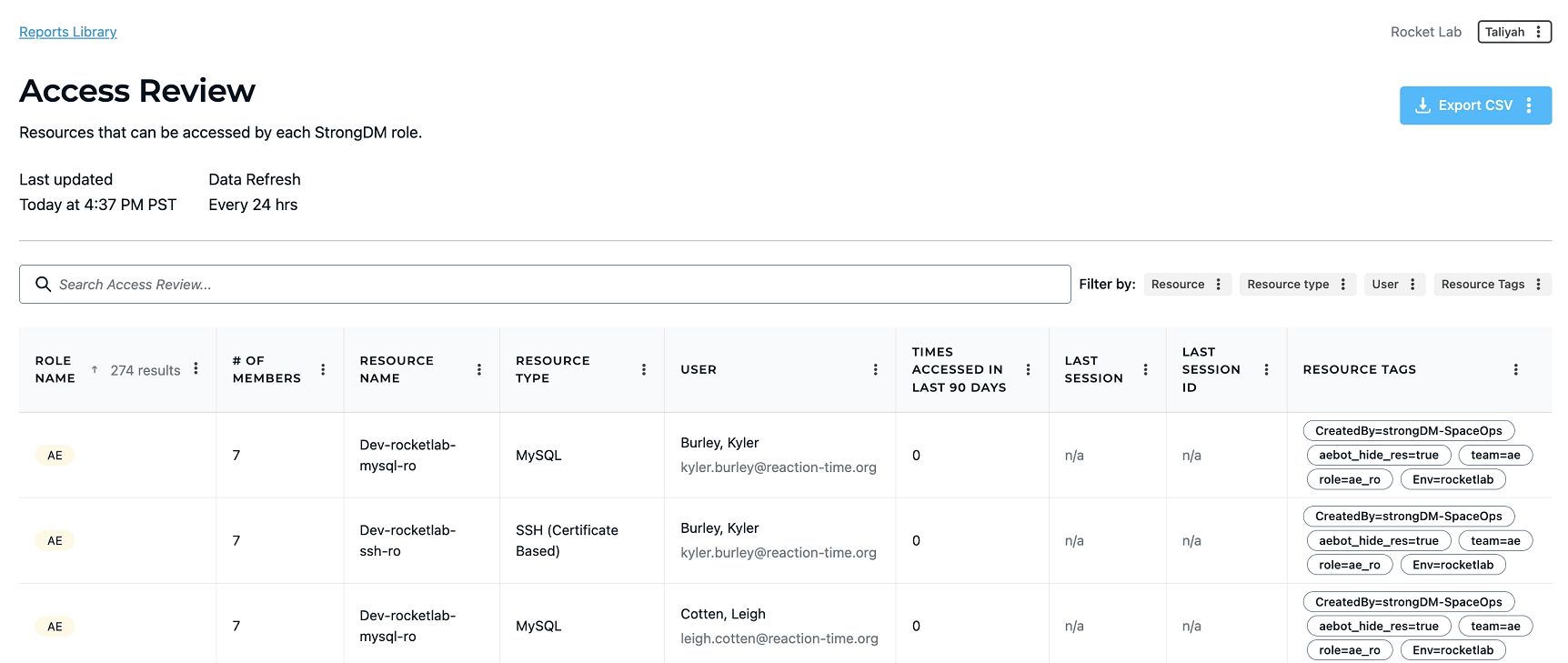
💡Make it easy: Root cause analysis is possible with granular audit logs that track every activity and query. Use StrongDM’s access review reports to easily view who has access to what and the commands executed. No need to check multiple resources. Everything is logged in one central access control plane. Try it yourself.
4. Employee Training
One of the fundamental building blocks of an organization’s cybersecurity risk posture is cybersecurity awareness amongst employees. That’s why insurers often require businesses to provide regular cybersecurity training to ensure employees understand their role in protecting data and systems.
Cybersecurity training can be complicated and time-consuming. Streamlining and simplifying workflows can ease the training burden. This was the case for StrongDM customer Zefr. The company made extensive use of temporary technical hires working on more than 30 databases and struggled to onboard and offboard staff efficiently. StrongDM’s Zero Trust Privileged Access Management (PAM) platform removed every trace of friction for Zefr, saving time, minimizing the need for training, and slashing administrative overhead.
“Adoption happened overnight. StrongDM can discover databases and show users what they have access to in a single feed. A user can sign in via Okta or Google and immediately be ready to work. Engineers love it. The basic reality is that our engineers are in databases a lot. Before StrongDM, the workflow was awkward, but now, it is unambiguous where they are supposed to be.”
- Wes Tanner, Vice President, Engineering (source)
5. Multi-factor Authentication
To reduce the risk of unauthorized access to data, insurers may require businesses to implement multi-factor authentication for remote access to their systems.
This aligns with the increase in remote work and the proliferation of cloud computing across industries. These two phenomena effectively expand the threat landscape and increase the need to safeguard overall network security.
Multi-factor authentication provides layered protection by requiring users to provide two forms of verification before gaining access to systems or data. The first form is typically a password or pin. The second is more difficult—often impossible—for hackers to seize, being a physical token or device, or a fingerprint or other biometric marker.
6. Encryption
Insurers may require businesses to encrypt sensitive data to reduce the risk of data breaches.
The concept of encryption has a long and illustrious history. Julius Caesar provides one of the earliest use cases for the practice, using the so-called “Caesar cipher” in his private correspondence.
Encryption defends at-rest and in-transit data from being stolen or manipulated by scrambling it into code that can only be unlocked with a unique secret key. It’s a foundational aspect of cloud computing security.
7. Privileged Access Management
DevOps and engineering teams need access to critical infrastructure as they develop, test, and release each element. To prevent misuse or abuse of what may become a complex bird’s nest of privileged accounts and credentials spread over a labyrinth of databases, servers, clusters, web apps, and clouds, insurers may require businesses to implement privileged access management solutions.
Where large teams are at work, privileged access management bolsters cybersecurity by ensuring that only authorized team members have access to critical resources. In the event of an incident, a privileged access management solution can also help uncover the source of the incident and take action to avoid a recurrence.
Meet Cyber Insurance Requirements, Reduce Premiums and Risk with StrongDM
Choosing the right cyber insurance policy can be a minefield. With many aspects to consider, the last thing you want is to make the wrong choice—-or get entangled with tricky policy exclusions.
With StrongDM, you can be sure the right people have the right access to your most sensitive information at the right time—helping your business meet regulatory compliance standards, reduce cyber risks, and qualify for the best cyber insurance policy on the market.
Get started today with StrongDM.
Next Steps
StrongDM unifies access management across databases, servers, clusters, and more—for IT, security, and DevOps teams.
- Learn how StrongDM works
- Book a personalized demo
- Start your free StrongDM trial

Categories:

About the Author
Schuyler Brown, Chairman of the Board, began working with startups as one of the first employees at Cross Commerce Media. Since then, he has worked at the venture capital firms DFJ Gotham and High Peaks Venture Partners. He is also the host of Founders@Fail and author of Inc.com's "Failing Forward" column, where he interviews veteran entrepreneurs about the bumps, bruises, and reality of life in the startup trenches. His leadership philosophy: be humble enough to realize you don’t know everything and curious enough to want to learn more. He holds a B.A. and M.B.A. from Columbia University. To contact Schuyler, visit him on LinkedIn.
You May Also Like